South Africa Forms New Unity Government
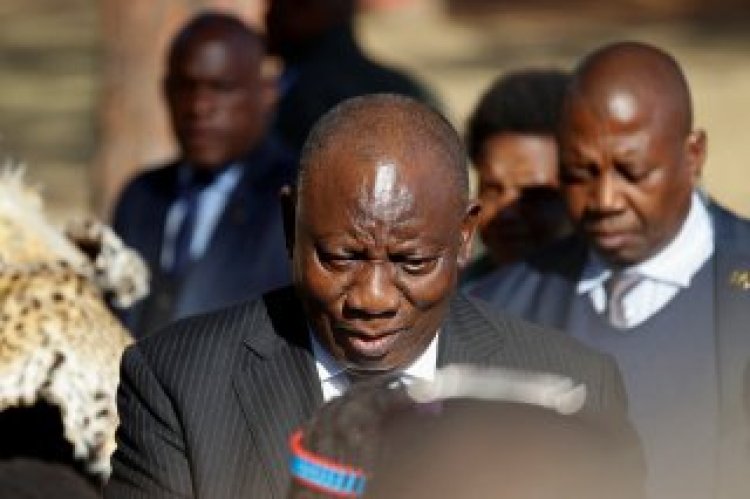

South Africa's new unity government inspired cautious optimism from industry and financial markets but many citizens and political analysts fear the coalition will struggle to deliver economic growth and social change.
President Cyril Ramaphosa appointed former main opposition leader John Steenhuisen to head an important ministry, bringing the Democratic Alliance and other parties into a coalition cabinet for the first time in three decades.
The ruling African National Congress was forced to join rival parties to stay in power after losing its majority in a May 29 poll, getting just 40% of the vote, the first time it has received under half of votes in a national election.
The compromise left the DA with six ministries, including agriculture, a major part of South Africa's economy, which went to Steenhuisen, public works, environment and basic education. It also got six deputy minister posts, including finance, trade and energy.
"The sheer weight and spread of these twelve portfolios amount to a recognition that the DA has a meaningful and vital role to play in the reconstruction of our country," Steenhuisen said in a speech.
For some, especially business owners, bringing a center-right, overtly capitalist party into the fold was a welcome step forward.
Jee-A van der Linde at Oxford Economics called Ramaphosa's cabinet a "business-friendly outcome" but said it remained to be seen whether it could solve South Africa's economic woes.
For parties representing the interests of workers, the mood was even more guarded.
Some businesses seemed to share this fear, with the South African Chamber of Commerce and Industry warning key goals "will not be achievable if there is no meritocracy", while political analyst Daniel Silke decried a lack of "outside experts in key portfolios not beholden to political interests".