Supreme Court Limits Capitol Riot Charges
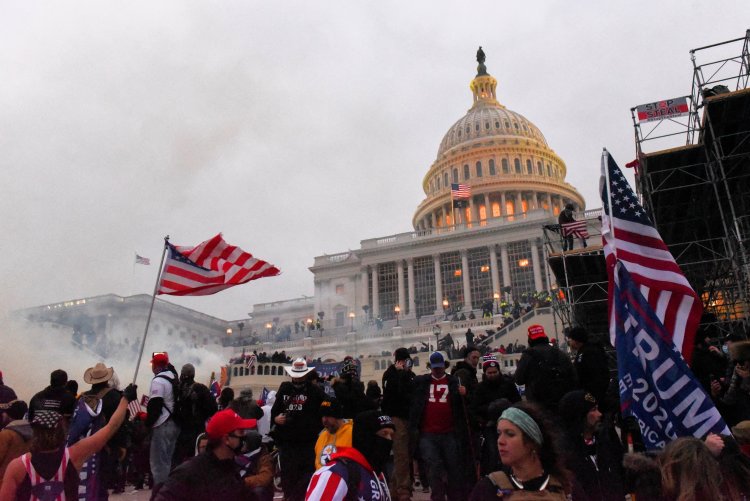

The Supreme Court made it harder to charge Capitol riot defendants with obstruction, a charge used in hundreds of prosecutions and also faced by former President Donald Trump.
The justices ruled 6-3 that the charge of obstructing an official proceeding, enacted in 2002 in response to the financial scandal that brought down Enron Corp., must include proof that defendants tried to tamper with or destroy documents. Only some of the people who violently attacked the Capitol on Jan. 6, 2021, fall into that category.
The decision could be used as fodder for claims by Trump and his Republican allies that the Justice Department has treated the Capitol riot defendants unfairly.
It's unclear how the court's decision will affect the case against Trump in Washington, although special counsel Jack Smith has said the charges faced by the former president would not be affected.
The high court returned the case of former Pennsylvania police officer Joseph Fischer to a lower court to determine if Fischer can be charged with obstruction.
Fischer is among about 350 people who have been charged with obstruction. Some pleaded guilty to or were convicted of lesser charges.
Chief Justice John Roberts wrote the court's opinion, joined by conservative Justices Samuel Alito, Neil Gorsuch, Brett Kavanaugh and Clarence Thomas, and by liberal Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson.
Trump posted on his Truth Social platform shortly after the decision, calling the ruling “Big News!” He shared another message that described the ruling as a “massive victory” for “J6 political prisoners.”
Roughly 170 Capitol insurrection defendants have been convicted of obstructing or conspiring to obstruct the Jan. 6 joint session of Congress, including the leaders of two far-right extremist groups, the Proud Boys and the Oath Keepers. A number of defendants have had their sentences delayed until after the justices rule on the matter.
Most lower court judges who have weighed in have allowed the charge to stand.